Our current data suggest that prolonged incubation with atropine alone followed by washing results in marked changes in NMS affinity and maximal binding as well as antagonism of carbachol-mediated PI hydrolysis. While the co-incubation of atropine with xanomeline during the 23h wait period resulted in similar effects on binding and function, divergent effects were observed when atropine was present during the initial pretreatment period. Xanomeline-induced changes in binding were unaffected by the Folinic acid calcium salt pentahydrate presence of atropine during the initial pretreatment period, whereas the functional effects of xanomeline on carbachol potency were abolished. An increase in basal response was also observed in this pretreatment paradigm, further complicating interpretation of these results. Several other pieces of Orbifloxacin evidence support the need for a functional receptor to elicit long-term changes observed following long-term treatments with xanomeline. Our laboratory has previously reported that point mutation of arginine-123 in the rat M1 receptor sequence results in nearly complete loss of receptor function. Using this cell line, we have shown that a functional receptor is not necessary for xanomeline persistent binding to occur. However, the appearance of a second high-potency binding site is not evident following long-term treatments in the mutant receptors, suggesting that these long-term changes are dependent on receptor activation. Furthermore, long-term changes in receptor availability are eliminated by this mutation. However, changes in NMS affinity are still evident, which may be due to interference by persistently-bound xanomeline independent of receptor activation. In conclusion, we have shown that acute as well as chronic xanomeline exposure results in long-term changes in M1 receptor binding and functional properties. Persistent binding of xanomeline elicits long-term changes in the receptor binding properties that are distinct from the profile obtained with carbachol, namely the appearance of a biphasic binding curve. We have demonstrated that pretreatment with high and low concentrations of xanomeline result in differential modes of receptor 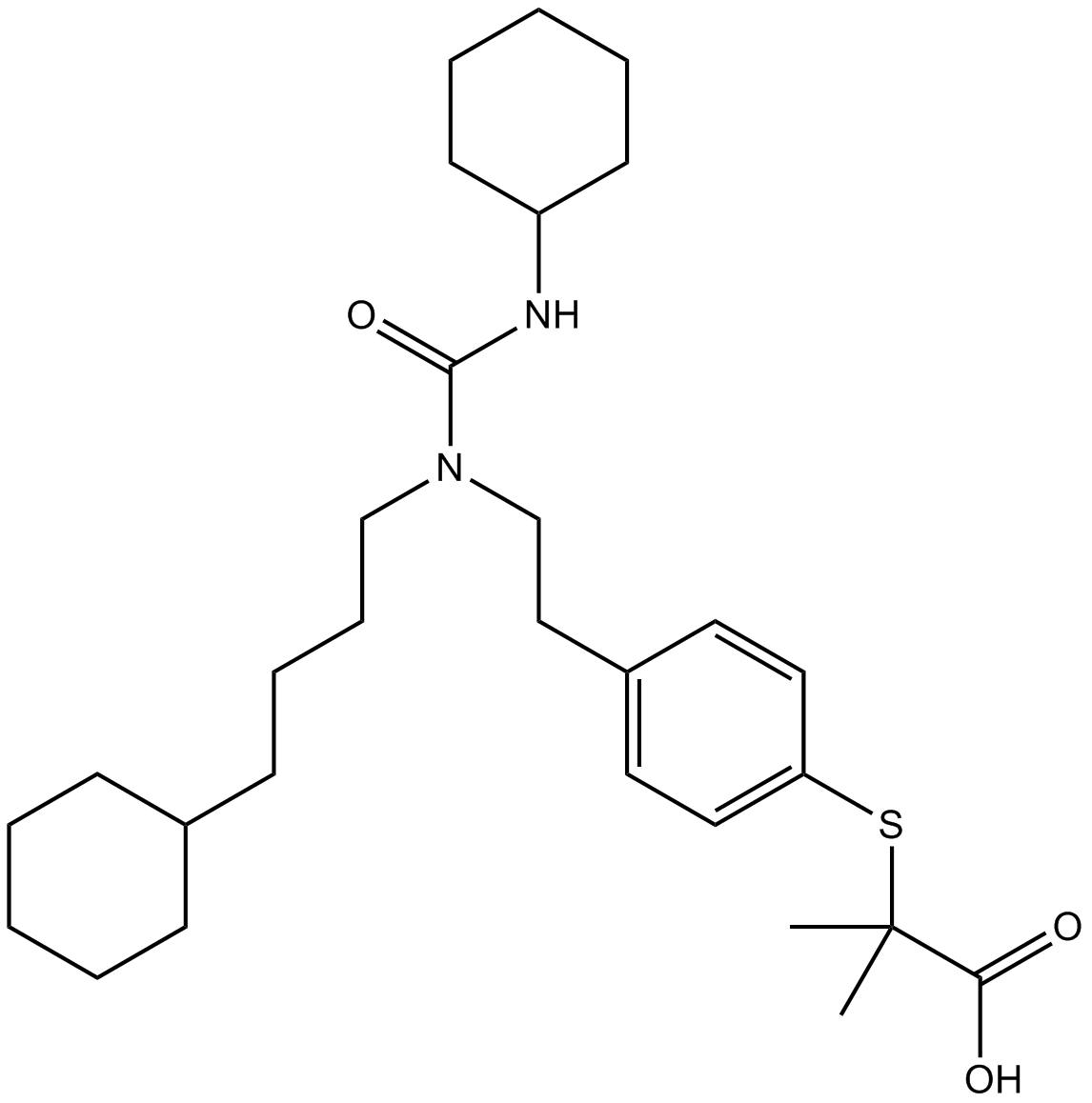 regulation. It is apparent that the effects observed at low concentrations of xanomeline are due, at least in part, to receptor down-regulation. DHA partially counteracts cognitive decline in the elderly. Moreover, omega-3 essential fatty acid-rich diets are associated with a trend in reduced risk for MCI and with MCI conversion to AD, whereas DHA has been shown to be beneficial in transgenic AD models. The 15-lipoxygenase-1- DHA-derived NPD1 displays neuroprotective bioactivity in brain and retinal cells against various insults, including oxidative injury, ischemia-reperfusion and inflammation. Both AD brain and the 3xTg-AD mouse exhibit reductions in DHA and NPD1. In this study we further characterized the antiinflammatory and anti-apoptotic activity of NPD1 in co-cultures of HNG cells stressed with Ab42 oligomer, and studied the NPD1mediated modulation of a- and b-secretase activity that resulted in reduced shedding of Ab42. AD is marked by synaptic damage, neuronal atrophy and cell death in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex. Neurotoxicity induced by Ab42 aggregates appears to drive microglial-mediated neuroinflammatory responses and apoptosis. Oxidative stress, calcium overload, mitochondrial dysfunction and membrane impairments, along with activation of caspases and cell death are associated with Ab42 up-regulation. We found that NPD1 induces HNG cell survival after Ab42oligomer-mediated stress and reduced Ab42-triggered apoptosis. NPD1 attenuated caspase-3 activation and decreased compacted nuclei and fragmented DNA. These observations are in agreement with the NPD1-mediated up-regulation of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2, Bcl-xl and Bfl-1 expression and the decrease in the pro-apoptotic expression of Bax, Bad and Bik. Neuroinflammatory neurodegeneration associated with Ab42 is an important contributory event to AD neuropathology.
regulation. It is apparent that the effects observed at low concentrations of xanomeline are due, at least in part, to receptor down-regulation. DHA partially counteracts cognitive decline in the elderly. Moreover, omega-3 essential fatty acid-rich diets are associated with a trend in reduced risk for MCI and with MCI conversion to AD, whereas DHA has been shown to be beneficial in transgenic AD models. The 15-lipoxygenase-1- DHA-derived NPD1 displays neuroprotective bioactivity in brain and retinal cells against various insults, including oxidative injury, ischemia-reperfusion and inflammation. Both AD brain and the 3xTg-AD mouse exhibit reductions in DHA and NPD1. In this study we further characterized the antiinflammatory and anti-apoptotic activity of NPD1 in co-cultures of HNG cells stressed with Ab42 oligomer, and studied the NPD1mediated modulation of a- and b-secretase activity that resulted in reduced shedding of Ab42. AD is marked by synaptic damage, neuronal atrophy and cell death in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex. Neurotoxicity induced by Ab42 aggregates appears to drive microglial-mediated neuroinflammatory responses and apoptosis. Oxidative stress, calcium overload, mitochondrial dysfunction and membrane impairments, along with activation of caspases and cell death are associated with Ab42 up-regulation. We found that NPD1 induces HNG cell survival after Ab42oligomer-mediated stress and reduced Ab42-triggered apoptosis. NPD1 attenuated caspase-3 activation and decreased compacted nuclei and fragmented DNA. These observations are in agreement with the NPD1-mediated up-regulation of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2, Bcl-xl and Bfl-1 expression and the decrease in the pro-apoptotic expression of Bax, Bad and Bik. Neuroinflammatory neurodegeneration associated with Ab42 is an important contributory event to AD neuropathology.
In addition to properties as an antagonist atropine is known to be an inverse agonist
Leave a reply