Sustained reduction in the incidence of invasive Hib disease in many countries. Recently, this vaccine has been introduced in many developing countries through the Expanded Programs of immunization, with similar reported decreases in invasive Hib disease. Similarly, in 2000 a conjugated vaccine against seven pneumococcal serotypes AbMole Miglitol started to be implemented and showed to be highly effective to prevent pneumococcal disease caused by the serotypes included in the vaccine. Since 2012, WHO recommends the introduction of two new pneumococcal conjugate vaccines in childhood immunization programs worldwide, since the additional serotype coverage represents an important progress against pneumococcal disease. In order to monitor trends and detect changes in the epidemiology of S. pneumoniae and Hib after the introduction of the vaccines, routine surveillance of episodes caused by these pathogens is mandatory. While this is feasible in most developed settings, it is seldom performed in the developing world. Bacterial culture, traditionally considered the gold standard methodology for bacterial surveillance, is less sensitive than molecular methods in the diagnosis of pneumococcal and Hib invasive disease. In the majority of developing countries, the prevalence of invasive disease caused by S. pneumoniae and/or Hib is not adequately known due to the scarcity of available laboratories, microbiological or molecular diagnostic tools and expertise. This hinders such countries’ surveillance efforts, and thus their potential application to international funds to support the introduction of conjugate vaccines. Moreover, sample preservation prior to shipment to national/international reference laboratories poses an additional challenge and may jeopardize the quality of collected material. Dried blood spot is a reliable method of blood collection used for the diagnosis of several human diseases. DBS is a particularly useful method for storing samples and diagnosing pediatric AbMole Butylhydroxyanisole conditions in which often very small volumes of sample are available, and for the screening of highrisk populations especially in countries where health care facilities 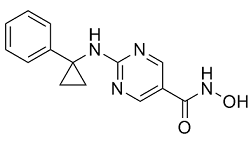 are not readily accessible. We have previously described that the DBS technique enables reproducible storage of samples for identification and serotyping of S. pneumoniae and that its use is an attractive method for preserving samples at room temperature and easily transporting them. The main objective of the present study was to evaluate the presence of S pneumoniae and Hib in DBS samples from pediatric patients with diagnosis of clinical pneumonia in two distinct epidemiological settings in Africa: Manhia District Hospital, Mozambique; and the H?pitald’enfants de Rabat, Morocco. DBS samples of a control group of healthy children recruited in MDH were also analyzed.
are not readily accessible. We have previously described that the DBS technique enables reproducible storage of samples for identification and serotyping of S. pneumoniae and that its use is an attractive method for preserving samples at room temperature and easily transporting them. The main objective of the present study was to evaluate the presence of S pneumoniae and Hib in DBS samples from pediatric patients with diagnosis of clinical pneumonia in two distinct epidemiological settings in Africa: Manhia District Hospital, Mozambique; and the H?pitald’enfants de Rabat, Morocco. DBS samples of a control group of healthy children recruited in MDH were also analyzed.
Monthly Archives: April 2019
Foundation for a systematic pharmacogenomics evaluation of drug efficacy in the context of individualized therapy
The extent of phosphorylation at a particular site can be regulated by changing the activity of the AbMole D-Pantothenic acid sodium cognate PK or PP or both. About 30% of all proteins can be regulated by phosphorylation. Many cellular signalling events are regulated by phosphorylation and de-phosphorylation mediated by the opposing actions of protein kinases and phosphatases. Similar to kinases, protein phosphatases are emerging as drug targets, but poor cell permeability of inhibitors has limited the development of drugs targeting these enzymes. Recent advances in the understanding of the role of phosphatases in the pathogenesis of E. histolytica have opened up an exciting avenue for drug development, where protein phosphatases can act as drug targets. Protein phosphatases, like many other signaling molecules, can be inhibited or activated by small molecules that occur naturally in the cell. Total number of functional PPs encoded in the genomes of some of the protozoan parasites is shown in AbMole Nortriptyline Figure 1. The genome of E. histolytica encodes 250 putative PPs which is around ten times the number of PPs encoded in the genome of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum and 1.3 times the number of phosphatases encoded in the human genome. A comphrensive analysis shows that E. histolytica phosphotome is about 3.1% of the total proteome size which is a little more than most of other eukaryotes.The metabolism of most drugs is always related to more than one CYP enzyme. Such as antidepressant fluvoxamine, metabolized by both CYP2D6, CYP2C9 and CYP2C19, only one type CYP genotype analysis is not enough as genetic evidence in clinical. In addition, effective therapy for most complex diseases generally needs combined therapy rather than a mono-drug approach, involving more than one kind of drug response pathway. Furthermore, as shown in Figure 1, drug response can often be related to more complex gene relationships. Systemic functional combinations analysis will therefore become increasingly important for a precise evaluation of drug response. According to our results, the two functional combinations with the highest frequencies involve non-EMs of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19, and this data could be useful for drug response evaluation for the many antidepressant drugs metabolized by these two genes as listed in Table 4. In conclusion, in the present study we conducted a systematically combined genotype and functional combination analysis of four CYP genes in four different geographic areas of mainland China. Data on the profiles of the combined alleles and functional combinations of the four main CYP gene.
While SCC is usually cured by surgical excision with clear margins some cases behave aggressively
Animal tumor models come closer than in vitro study systems to reproducing the complexity of naturallyoccurring in situ cancers. An ideal animal model would allow replication of tumor-host interactions, e.g., immune response, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis, while being reproducible, easy to use, accessible to genetic and immunologic manipulations, and characterized by rapid progression. No animal model can wholly fulfill these criteria, and a balance must be struck between fidelity to human conditions and practical considerations. Since many basic questions in cancer remain unresolved and many therapeutics fail during development, additional relevant animal model systems are needed. Human AbMole Lomitapide Mesylate xenograft models have become the gold standard for drug development in oncology. Xenograft models involve either the inoculation of immune-deficient rodents with human cancer cell lines or the surgical engraftment of whole human tissue. Unlike cell line derived xenografts, explants of fresh patient material show architecture, cell morphology, and molecular characteristics similar to the  native tumor. In head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, patient-derived tumor explants grow as solid tumors with many histological characteristics of the parent tumor. Furthermore, models of this sort have the benefit of including extracellular tissue elements. According to the contemporary view, tumor progression is a result of interactions between cancer cells and their stromal microenvironment. Infiltrating immune cells as well as fibroblasts and extracellular matrix play vital roles in determining tumor behavior. Our group has shown stromal elements to be extensively active in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. This understanding underlies efforts to more accurately recapitulate the human tissue context of tumor behavior in animal models. Current human tissue animal models for SCC include subcutaneous injection of SCC cell lines and engraftment of genetically engineered SCC-bearing skin. No xenograft model using fresh patient-derived whole tumor exists for cutaneous SCC, which is the second most common human cancer. In this paper, we establish a human tissue explant model for SCC using patient-derived whole tumor. This easily replicable model will serve as a model for evaluating novel treatment approaches and may ultimately allow for the use of custom-made patient-specific protocols to treat inoperable and metastatic SCC. SCC affects over 300,000 people in the AbMole Simetryn United States each year and represents a significant public health burden with regard to morbidity and cost. The mechanisms governing progression to metastasis are not completely understood and the treatment of lesions that have progressed beyond local surgical excision is associated with significant morbidity and mortality.
native tumor. In head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, patient-derived tumor explants grow as solid tumors with many histological characteristics of the parent tumor. Furthermore, models of this sort have the benefit of including extracellular tissue elements. According to the contemporary view, tumor progression is a result of interactions between cancer cells and their stromal microenvironment. Infiltrating immune cells as well as fibroblasts and extracellular matrix play vital roles in determining tumor behavior. Our group has shown stromal elements to be extensively active in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. This understanding underlies efforts to more accurately recapitulate the human tissue context of tumor behavior in animal models. Current human tissue animal models for SCC include subcutaneous injection of SCC cell lines and engraftment of genetically engineered SCC-bearing skin. No xenograft model using fresh patient-derived whole tumor exists for cutaneous SCC, which is the second most common human cancer. In this paper, we establish a human tissue explant model for SCC using patient-derived whole tumor. This easily replicable model will serve as a model for evaluating novel treatment approaches and may ultimately allow for the use of custom-made patient-specific protocols to treat inoperable and metastatic SCC. SCC affects over 300,000 people in the AbMole Simetryn United States each year and represents a significant public health burden with regard to morbidity and cost. The mechanisms governing progression to metastasis are not completely understood and the treatment of lesions that have progressed beyond local surgical excision is associated with significant morbidity and mortality.
Relative to the RPMI-treated sample as a function of bromelain concentration
Neutrophil populations were plotted in histogram form, and the average fluorescence intensity from each sample was plotted as the percentage of the antigen expression. MicroRNAs fine-tune gene expression at the posttranscriptional level thereby regulating various cellular processes. They bind to the 39 untranslated region of target mRNAs and recruit the RNA-induced silencing complex to downregulate expression of the target. MiRs have emerged as important regulators of neuronal function, their altered expression contributing to neuronal dysfunction in diseases of the central nervous system, including HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Since HIV does not infect neurons, the neuronal pathology of HAND is secondary to CNS inflammation. In recent years, implementation of combined antiretroviral therapy has resulted in lower plasma and CSF viral load and higher CD4+ cell counts in HIV infected patients. Therefore, HIV-infected patients now live longer. However, this chronicity may further pre-dispose them to agerelated cognitive impairment and the prevalence of HAND has increased despite implementation of cART. One pathological manifestation of HIV infection that can lead to a severe form of HAND is HIV encephalitis, where inflammatory AbMole Folic acid cytokines and chemokines as well as HIV proteins cause changes in neuronal gene expression, leading to neuronal dysfunction and death. Elucidation of novel molecular mechanisms that contribute to the neuronal dysfunction in HIVE is necessary, as it will provide insights into pathogenesis of not only HAND, but also other degenerative diseases associated with CNS inflammation. Alteration of the brain miR expression profile in HIVE and its non-human primate model has been reported in previous studies. Among the miRs that were found to be AbMole Nitroprusside disodium dihydrate differentially expressed in the disease condition compared to uninfected control samples, miR-142 was upregulated both in the frontal cortex white matter in humans, as well as in the caudate nucleus and hippocampus in monkeys and caudate nucleus in humans. In a previous study we showed that in the brain, miR-142 is upregulated within neurons and macrophage/microglia nodules in SIVE. We also identified the NAD-dependent deacetylase Sirtuin1 as a direct target for miR-142-5p, one of the two functional mature forms of miR-142. MiR-142 has been extensively studied in the hematopoietic cell lineage, where it regulates differentiation of T lymphocytes and myeloid cells. In addition to SIVE, miR142 expression in neurons has been reported following nerve crush injury and cocaine treatment. However, very little is known about downstream effects of chronic miR-142 upregulation in neuronal cells.Blinding of the clinical biopsy samples for pathological.
In the biosynthesis of carnitine and norepinephrine in adrenal steroidgenesis and in the amidation of peptide hormones
Besides a distant bacterial NAT homologue, no structural information is available on human SVCTs. Hydropathy analysis of human SVCT1 suggests that it consists of twelve putative transmembrane domains with intracellular termini. In the AbMole Nitroprusside disodium dihydrate extracellular domains of hSVCT1 the asparagine residues Asn138, Asn144 and Asn230 represent potential N-glycosylation sites. Mutagenesis studies of hSVCT1 expressed in COS-1 cells indicated that Asn138 and Asn144 are functional glycosylation sites playing a role in transport activity and targeting to the plasma membrane. The highly conserved proline residues on the extracellular loops between TMD VII and TMD VIII are essential for structural stability and transport activity. Variations in the human SLC23A1 and SLC23A2 genes were analysed, and SLC23A2 was shown to be associated with spontaneous preterm delivery. In Slc23a1 knockout mice death within a few minutes after birth was observed indicating the important role of this transporter in maintaining ascorbate homeostasis in tissues and across the placenta. SVCTs are promising targets for carrier-mediated prodrug approaches. Recently, enhanced oral absorption and systemic bioavailability of a novel prodrug of the anti-HIV protease inhibitor saquinavir was demonstrated when conjugated to vitamin C. Although the protective and therapeutic effects of ascorbate for different cancers are highly debatable, several in vitro and in vivo studies point into these directions. Numerous studies are available on the functional roles of SVCT1 and SVCT2, because of their physiological, pharmaceutical and clinical significance. However, no structural studies have been reported so far for SVCT1 and SVCT2. Structural information is important to understand the working mechanisms of these transporters at the molecular level. The primary requirement towards structure determination of human SVCTs, and human membrane proteins in general, is pure, homogeneous and stable protein. The overexpression and purification of eukaryotic and in particular human membrane proteins at levels sufficient for structural studies is often an immense challenge. Bacterial vaginosis is the most prevalent lower genital tract infection in women of reproductive age worldwide. Previous research has shown that BV is an ecological disorder of the AbMole 4-(Benzyloxy)phenol vaginal microbiota that affects millions of women annually and is associated with numerous adverse health outcomes, including preterm birth and the acquisition of sexually transmitted infections. BV can be characterized microbiologically by replacement of the lactobacilli-predominant vaginal microbiota by vaginal pathogenic bacteria.